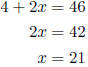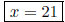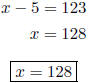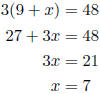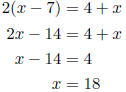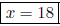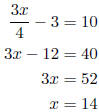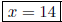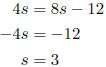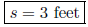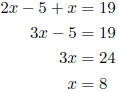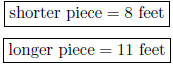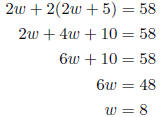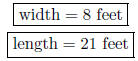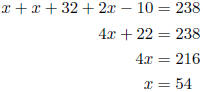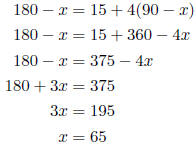- Home
- INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA
- Course Syllabus for Algebra I
- Mid-Plains Community College
- FRACTION OF A WHOLE NUMBER
- Systems of Linear Equations
- MATH FIELD DAY
- Course Outline for Finite Mathematics
- Calculus
- Algebra Final Examination
- Math 310 Exam #2
- Review of Trigonometric Functions
- Math 118 Practice test
- Precalculus Review
- Section 12
- Literal Equations
- Calculus Term Definitions
- Math 327A Exercise 2
- Public Key Algorithms II
- Maximizing Triangle Area
- Precalculus I Review for Midterm
- REVIEW OF A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA
- Math 6310 Homework 5
- Some Proofs of the Existence of Irrational Numbers
- ALGEBRAIC PROPERTIES OF MATRIX OPERATIONS
- Math 142 - Chapter 2 Lecture Notes
- Math 112 syllabus
- Math 371 Problem Set
- Complex Numbers,Complex Functions and Contour Integrals
- APPLICATIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
- Week 4 Math
- Fractions
- Investigating Liner Equations Using Graphing Calculator
- MATH 23 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
- Algebra 1
- PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM AND DISTANCE FORMULA
- Georgia Performance Standards Framework for Mathematics - Grade 6
- Intermediate Algebra
- Introduction to Fractions
- FACTORINGS OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
- Elementary Algebra Syllabus
- Description of Mathematics
- Integration Review Solutions
- College Algebra - Applications
- A Tip Sheet on GREATEST COMMON FACTOR
- Syllabus for Elementary Algebra
- College Algebra II and Analytic Geometry
- Functions
- BASIC MATHEMATICS
- Quadratic Equations
- Language Arts, Math, Science, Social Studies, Char
- Fractions and Decimals
- ON SOLUTIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
- Math 35 Practice Final
- Solving Equations
- Introduction to Symbolic Computation
- Course Syllabus for Math 935
- Fractions
- Fabulous Fractions
- Archimedean Property and Distribution of Q in R
- Algebra for Calculus
- Math112 Practice Test #2
- College Algebra and Trigonometry
- ALGEBRA 1A TASKS
- Description of Mathematics
- Simplifying Expressions
- Imaginary and Complex Numbers
- Building and Teaching a Math Enhancement
- Math Problems
- Algebra of Matrices Systems of Linear Equations
- Survey of Algebra
- Approximation of irrational numbers
- More about Quadratic Functions
- Long Division
- Algebraic Properties of Matrix Operation
- MATH 101 Intermediate Algebra
- Rational Number Project
- Departmental Syllabus for Finite Mathematics
- WRITTEN HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT
- Description of Mathematics
- Rationalize Denominators
- Math Proficiency Placement Exam
- linear Equations
- Description of Mathematics & Statistics
- Systems of Linear Equations
- Algebraic Thinking
- Study Sheets - Decimals
- An Overview of Babylonian Mathematics
- Mathematics 115 - College Algebra
- Complex Numbers,Complex Functions and Contour Integrals
- Growing Circles
- Algebra II Course Curriculum
- The Natural Logarithmic Function: Integration
- Rational Expressions
- QUANTITATIVE METHODS
- Basic Facts about Rational Funct
- Statistics
- MAT 1033 FINAL WORKSHOP REVIEW
- Measurements Significant figures
- Pre-Calculus 1
- Compositions and Inverses of Functions
APPLICATIONS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
Key Words:
• Addition - sum, added to, increased by, more than
• Subtraction - difference, minus, decreased by, subtracted from
• Multiplication - product, times, double (2x), tripled (3x)
• Division - quotient, ratio, divided by
Formulas:
• Area of square:
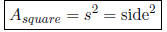
• Area of a rectangle:
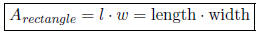
• Area of a triangle:
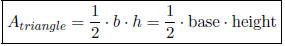
• Area of a trapezoid:
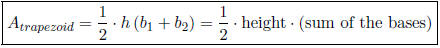
• Area of a circle:
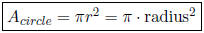
• Perimeter:
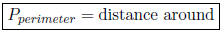
In other words, add each side together.
• Circumference of a circle:
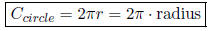
Angle Properties:
• Vertical Angles are opposite angles formed by intersecting lines.
Vertical angles always have the
same measurement.
• Complementary Angles are two angles whose sum is 90°.
• Supplementary Angles are two angles whose sum is 180°.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
• For perimeter, be sure to add EACH AND EVERY side in the formula.
• Be very careful to translate the problem into correct mathematical form. When
it has been translated,
you should be able to read it back.
• Be careful: a minus b is translated a - b; whereas, a less than b is
translated b - a.
• Be careful on the difference between these two statements:
- The sum of four times a number and 5 is translated 4x + 5.
- Four times the sum of a number and 5 is translated 4(x + 5).
• Make sure that you answer the question being asked. If it asks for two
answers, give both.
PROBLEMS
|
1. The sum of four and twice a number is 46. Find the number. Let x = the number.
|
3. A number decreased by 15 is 123. Find the number. Let x = the number.
|
|
2. Three times the sum of nine and a number is 48. Find the number. Let x = the number.
|
4. If seven is subtracted from a number and this difference is doubled, the result is four more than the number. Find the number. Let x = the number.
|
|
5. If the quotient of three times a number and four is decreased by three, the result is ten. Find the number. Let x = the number.
|
7. A stained-glass window in a church is in the shape of a square. The perimeter of the square is eight times the length of a side in feet, decreased by twelve. Find the length of a side of the window. Let
|
|
6. A 19 foot piece of string is cut into two pieces so that one piece is five feet shorter than twice the shorter piece. Find the length of both pieces. Let x = the shorter piece
|
8. The length of a rectangular shaped garden is five feet more than twice the width. The perimeter is 58 feet. Find the length and width of the garden. Let w = the width of the garden.
|
|
9. A lot is in the shape of a triangle. One side is 32 feet longer than the shortest side while the third side is ten feet shorter than twice the shorter side. The perimeter of the lot is 238 feet. Find the length of the sides of the lot. Let x = the shortest side.
|
10. The supplement of an angle measure 15° more than four times its complement. Find the measure of the angle. Let x = the degree measure of the angle.
|